반응형
1. 여러가지 자료구조
자료구조란? ( Data Structure )
- 프로그램에서 사용할 많은 데이터를 메모리 상에서 관리하는 여러 구현방법들
- 효율적인 자료구조가 성능 좋은 알고리즘의 기반이 됨
- 자료의 효율적인 관리는 프로그램의 수행속도와 밀접한 관련이 있음
- 여러 자료 구조 중에서 구현하려는 프로그램에 맞는 최적의 자료구조를 활용해야 하므로
자료구조에 대한 이해가 중요.
자료 구조에는 어떤 것들이 있나
- 한 줄로 자료를 관리하기 ( 선형 자료구조 )
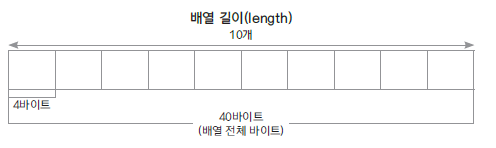
배열 ( Array )
- 선형으로 자료를 관리
- 정해진 크기의 메모리를 먼저 할당받아 사용
- 자료의 물리적 위치와 논리적 위치가 같음
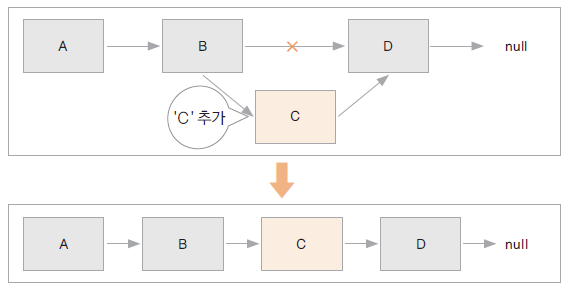
연결 리스트 ( LinkedList )
- 선형으로 자료를 관리
- 자료가 추가될 때마다 메모리를 할당 받고 자료는 링크로 연결된다
- 자료의 물리적 위치와 논리적 위치가 다를 수 있다
리스트에 자료 추가하기
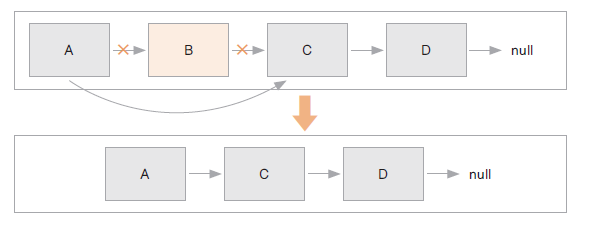
리스트에서 자료 삭제
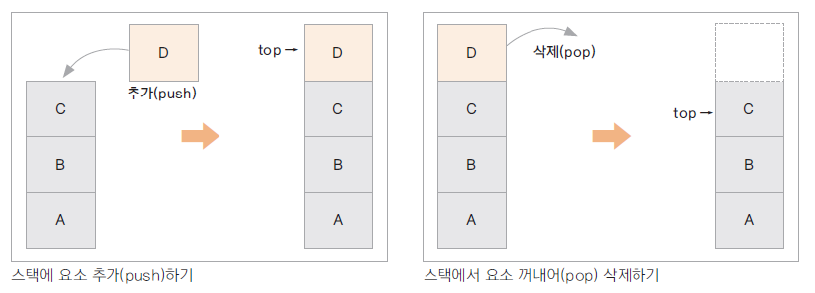
스택 ( Stack )
- 가장 나중에 입력된 자료가 가장 먼저 출력되는 자료 구조 ( LIFO )
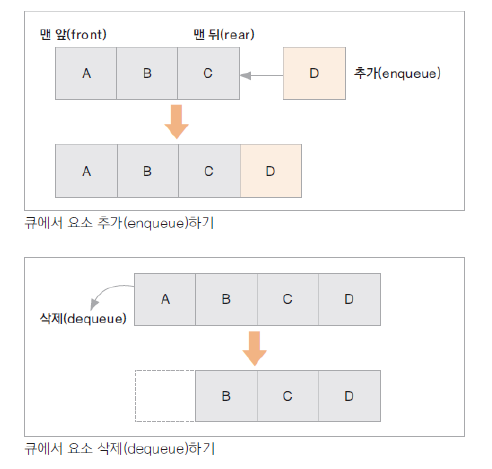
큐 ( Queue )
- 가장 먼저 입력된 자료가 가장 먼저 출력되는 자료 구조 ( FIFO )
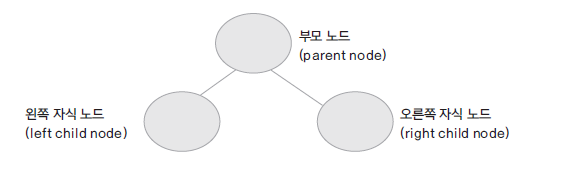
트리 ( Tree )
- 부모 노드와 자식 노드간의 연결로 이루어진 자료 구조
힙 ( Heap )
- Priority queue를 구현 ( 우선 큐 )
- Max heap : 부모 노드는 자식 노드보다 항상 크거나 같은 값을 갖는 경우
- Min heap : 부모 노드는 자식 노드보다 항상 작거나 같은 값을 같는 경우
이진 트리 ( binary tree )
- 부모노드에 자식노드가 두개 이하인 트리
이진 검색 트리 ( binary search tree )
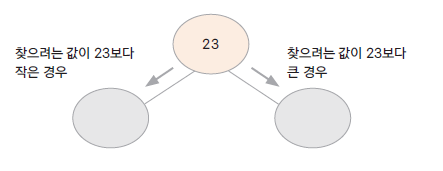
자료(key)의 중복을 허용하지 않음
왼쪽 자식 노드는 부모 노드보다 작은 값, 오른쪽 자식 노드는 부모 노드보다 큰 값을 가짐
자료를 검색에 걸리는 시간이 평균 log(n) 임
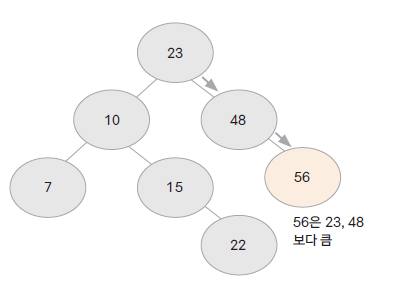
inorder traversal 탐색을 하게 되면 자료가 정렬되어 출력됨ex) [ 23, 10, 48, 15, 7, 22, 56 ] 순으로 자료를 넣을 때 BST
- JDK 클래스 : TreeSet, TreeMap ( Tree로 시작되는 클래스는 정렬을 지원 함 )
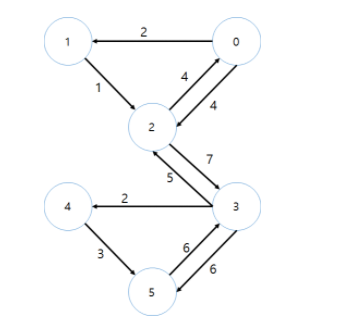
그래프 ( Graph )
- 정점과 간선들의 유한 집합 G = ( V,E)
- 정점 ( vertex ) : 여러 특성을 가지는 객체, 노드(node)
- 간선( edge ) : 이 객체들의 연결관계를 나타냄, 링크(link)
- 간선은 방향성이 있는 경우와 없는경우가 있다.
- 그래프를 구현하는 방법 : 인접 행렬 ( adjacency matrix ), 인접 리스트( adjacency list )
- 그래프를 탐색하는 방법 : BFS( bread first search ), DFS( depth first search )
그래프의 예
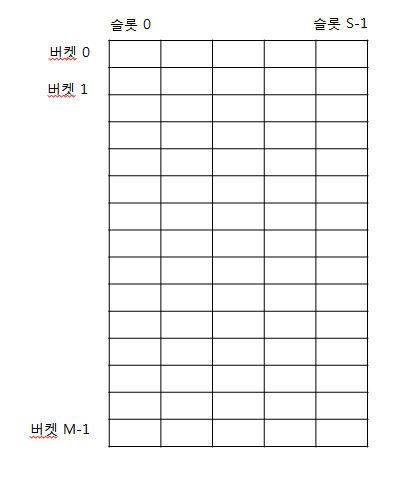
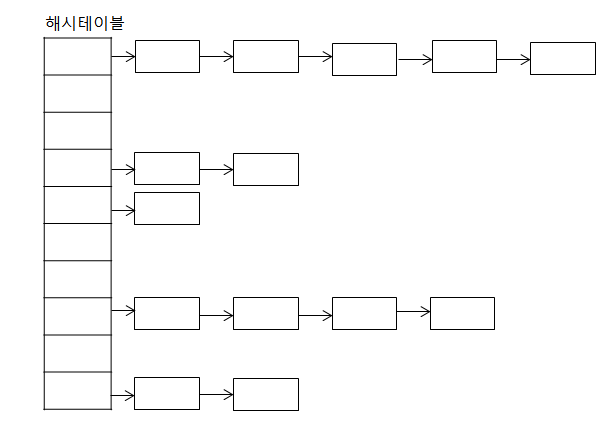
해싱 ( hashing )
- 자료를 검색하기 위한 자료구조
- 검색을 위한 자료구조
- 키(key)에 대한 자료를 검색하기 위한 사전(dictionary)개념의 자료구조
- key는 유일하고 이에 대한 value를 쌍으로 저장
- index = h(key) : 해시 함수가 key에 대한 인덱스를 반환해줌, 해당 인덱스 위치에 자료를 저장하거나 검색하게 됨
- 해시 함수에 의해 인덱스 연산이 산술적으로 가능 O(1)
- 저장 되는 메모리 구조를 해시테이블 이라고 함
- JDK 클래스 : HashMap, Properties
2. 배열 ( Array ) 구현하기
Array의 특징
- 동일한 데이터 타입을 순서에 따라 관리하는 자료구조
- 정해진 크기가 있음
- 요소의 추가와 제거시 다른 요소들의 이동이 필요함
- 배열의 i번째 요소를 찾는 인덱스 연산이 빠름
- jdk 클래스 : ArrayList, Vector
Array 구현
MyArray.java
public class MyArray {
int[] intArr; //int array
int count; //개수
public int ARRAY_SIZE;
public static final int ERROR_NUM = -999999999;
public MyArray()
{
count = 0;
ARRAY_SIZE = 10;
intArr = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
}
public MyArray(int size)
{
count = 0;
ARRAY_SIZE = size;
intArr = new int[size];
}
public void addElement(int num)
{
if(count >= ARRAY_SIZE){
System.out.println("not enough memory");
return;
}
intArr[count++] = num;
}
public void insertElement(int position, int num)
{
int i;
if(count >= ARRAY_SIZE){ //꽉 찬 경우
System.out.println("not enough memory");
return;
}
if(position < 0 || position > count ){ //index error
System.out.println("insert Error");
return;
}
for( i = count-1; i >= position ; i--){
intArr[i+1] = intArr[i]; // 하나씩 이동
}
intArr[position] = num;
count++;
}
public int removeElement(int position)
{
int ret = ERROR_NUM;
if( isEmpty() ){
System.out.println("There is no element");
return ret;
}
if(position < 0 || position >= count ){ //index error
System.out.println("remove Error");
return ret;
}
ret = intArr[position];
for(int i = position; i<count -1; i++ )
{
intArr[i] = intArr[i+1];
}
count--;
return ret;
}
public int getSize()
{
return count;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
if(count == 0){
return true;
}
else return false;
}
public int getElement(int position)
{
if(position < 0 || position > count-1){
System.out.println("검색 위치 오류. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count +"개 입니다.");
return ERROR_NUM;
}
return intArr[position];
}
public void printAll()
{
if(count == 0){
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없습니다.");
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<count; i++){
System.out.println(intArr[i]);
}
}
public void removeAll()
{
for(int i=0; i<count; i++){
intArr[i] = 0;
}
count = 0;
}
}MyArrayTest.java
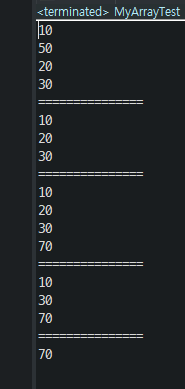
public class MyArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray array = new MyArray();
array.addElement(10);
array.addElement(20);
array.addElement(30);
array.insertElement(1, 50);
array.printAll();
System.out.println("===============");
array.removeElement(1);
array.printAll();
System.out.println("===============");
array.addElement(70);
array.printAll();
System.out.println("===============");
array.removeElement(1);
array.printAll();
System.out.println("===============");
System.out.println(array.getElement(2));
}
}MyObjectArray.java
public class MyObjectArray {
private int cout;
private Object[] array;
public int ARRAY_SIZE;
public MyObjectArray()
{
ARRAY_SIZE = 10;
array = new Object[ARRAY_SIZE];
}
public MyObjectArray(int size)
{
ARRAY_SIZE = size;
array = new Object[ARRAY_SIZE];
}
}
3. 연결 리스트 ( LinkedList ) 구현하기
LinkedList 특징
- 동일한 데이터 타입을 순서에 따라 관리하는 자료구조
- 자료를 저장하는 노드에는 자료와 다음 요소를 가리키는 링크(포인트)가 있음
- 자료가 추가될 때 노드 만큼의 메모리를 할당 받고 이전 노드의 링크로 연결함 (정해진 크기가 없음)
- 연결 리스트의 i번째 요소를 찾는게 걸리는 시간은 요소의 개수에 비례 : O(n)
- jdk 클래스 : LinkedList
LinkedList 구현
MyListNode.java
public class MyListNode {
private String data; // 자료
public MyListNode next; // 다음 노드를 가리키는 노드
public MyListNode() {
data = null;
next = null;
}
public MyListNode(String data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public MyListNode(String data, MyListNode link) {
this.data = data;
this.next = link;
}
public String getData() {
return data;
}
}MyLinkedList.java
public class MyLinkedList {
private MyListNode head;
int count;
public MyLinkedList() {
head = null;
count = 0;
}
public MyListNode addElement(String data) {
MyListNode newNode;
if(head == null) { // 맨 처음일 때
newNode = new MyListNode(data);
head = newNode;
} else {
newNode = new MyListNode(data);
MyListNode temp = head;
while(temp.next != null) { // 맨 뒤로 가서
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
}
count++;
return newNode;
}
public MyListNode insertElement(int position, String data) {
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
MyListNode preNode = null;
MyListNode newNode = new MyListNode(data);
if(position <0 || position > count) {
System.out.println("추가할 위치 오류입니다. 현재 리스트의 갯수는" + count + " 개 입니다.");
return null;
}
if(position == 0) { // 맨앞에 들어갈 경우
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
} else {
for(i=0; i<position; i++) {
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
newNode.next = preNode.next;
preNode.next = newNode;
}
count++;
return newNode;
}
public MyListNode removeElement(int position) {
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
MyListNode preNode = null;
if (position >= count) {
System.out.println("삭제할 위치 오류입니다. 현재 리스트의 갯수는" + count + " 개 입니다.");
return null;
}
if (position == 0) { // 맨 앞을 삭제
head = tempNode.next;
} else {
for(i=0; i<position; i++) {
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
preNode.next = tempNode.next;
}
count--;
System.out.println(position + "번 째 항목 삭제 되었습니다.");
return tempNode;
}
public String getElement(int position)
{
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
if(position >= count ){
System.out.println("검색 위치 오류 입니다. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count +"개 입니다.");
return new String("error");
}
if(position == 0){ //맨 인 경우
return head.getData();
}
for(i=0; i<position; i++){
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
return tempNode.getData();
}
public void printAll()
{
if(count == 0){
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없습니다.");
return;
}
MyListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null){
System.out.print(temp.getData());
temp = temp.next;
if(temp!=null){
System.out.print("->");
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
public int getSize()
{
return count;
}
public void removeAll()
{
head = null;
count = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(head==null) return true;
else return false;
}
}MyLinkedListTest.java
public class MyLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();
list.addElement("A");
list.addElement("B");
list.addElement("C");
list.printAll();
list.insertElement(3,"D");
list.printAll();
list.removeElement(0);
list.printAll();
list.removeElement(1);
list.printAll();
list.insertElement(0, "A-1");
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.removeElement(0);
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.removeAll();
list.printAll();
list.addElement("A");
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.getElement(0));
list.removeElement(0);
}
}
4. 스택 구현하기
Stack의 특징
- 맨 마지막 위치(top)에서만 자료를 추가, 삭제, 꺼내올 수 있음( 중간 자료를 꺼낼 수 없다 )
- LIFO (후입 선출)구조
- 택배 상자가 쌓여있는 모양
- 가장 최근의 자료를 찾아오거나 게임에서 히스토리를 유지하고 이를 무를 때 사용이 가능함
- 함수의 메모리는 호출 순서에 따른 stack 구조
- JDK 클래스 : Stack
배열을 사용하여 Stack 구현
MyArrayStack.java
import ch02.MyArray;
public class MyArrayStack {
MyArray arrayStack;
int top;
public MyArrayStack() {
top = 0;
arrayStack = new MyArray();
}
public MyArrayStack(int size) {
top = 0;
arrayStack = new MyArray(size);
}
public void push(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Stack is Full");
return;
}
arrayStack.addElement(data);
top++;
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
return MyArray.ERROR_NUM;
}
return arrayStack.removeElement(--top);
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
return MyArray.ERROR_NUM;
}
return arrayStack.getElement(--top);
}
public boolean isFull() {
if ( top == arrayStack.ARRAY_SIZE ) {
return true;
} else return false;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if ( top == 0 ) {
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
return true;
} else return false;
}
public void printAll() {
arrayStack.printAll();
}
}MyArraySatckTest.java
public class MyArrayStackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
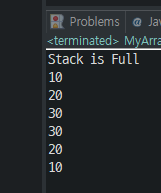
MyArrayStack stack = new MyArrayStack(3);
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(40);
stack.printAll();
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
}
5. 큐 ( Queue ) 구현하기
Queue의 특징
- 맨 앞(front)에서 자료를 꺼내거나 삭제하고, 맨 뒤(rear)에서 자료를 추가함
- FIFO (선입선출)구조
- 일상 생활에서 1열로 줄 서있는 모양
- 순차적으로 입력된 자료를 순서대로 처리하는데 많이 사용되는 자료구조
- 콜 센터에 들어온 문의전화, 메세지 큐 등에 활용됨
- JDK클래스 : ArrayList
연결 리스트를 활용하여 Queue구현하기
MyLinkedQueue.java
import ch03.MyLinkedList;
import ch03.MyListNode;
interface Queue {
public void enQueue(String data);
public String deQueue();
public void printQueue();
}
public class MyLinkedQueue extends MyLinkedList implements Queue {
MyListNode front;
MyListNode rear;
@Override
public void enQueue(String data) {
MyListNode newNode;
if(isEmpty()) {
newNode = addElement(data);
front = newNode;
rear = newNode;
} else {
newNode = addElement(data);
rear = newNode;
}
System.out.println(newNode.getData() + " added");
}
@Override
public String deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Empty");
return null;
}
String data = front.getData();
front = front.next;
if ( front == null ) {
rear = null;
}
return data;
}
@Override
public void printQueue() {
printAll();
}
}MyLinkedQueueTest.java
public class MyLinkedQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
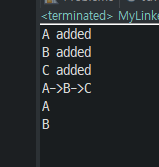
MyLinkedQueue listQueue = new MyLinkedQueue();
listQueue.enQueue("A");
listQueue.enQueue("B");
listQueue.enQueue("C");
listQueue.printAll();
System.out.println(listQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println(listQueue.deQueue());
}
}
반응형
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바의 다양한 기능 / 내부 클래스 정의, 람다식 (0) | 2022.12.02 |
|---|---|
| 자바와 자료구조 / Generic, T extends, 컬렉션 프레임워크 (0) | 2022.11.30 |
| 자바의 유용한 클래스 / Object, String, StringBuilder, StringBuffer, textblock, Class 클래스 (0) | 2022.11.22 |
| Java 객체지향 핵심 / 다운 캐스팅, 추상클래스, 추상클래스 응용, 인터페이스, DAO, 인터페이스 상속 (1) | 2022.11.18 |
| Java 객체 지향 핵심 / 상속, 형 변환, 재정의(override), 다형성 (0) | 2022.11.17 |



